🛡VPN: What is It & How Does it Work?
Explain VPN networks and how they work internally.
Hi, I’m Wajid Khan. I am trying to explain computer stuff in a simple and engaging manner, so that even non-techies can easily understand, and delivered to your inbox weekly. Join me on an under-the-hood tech journey.
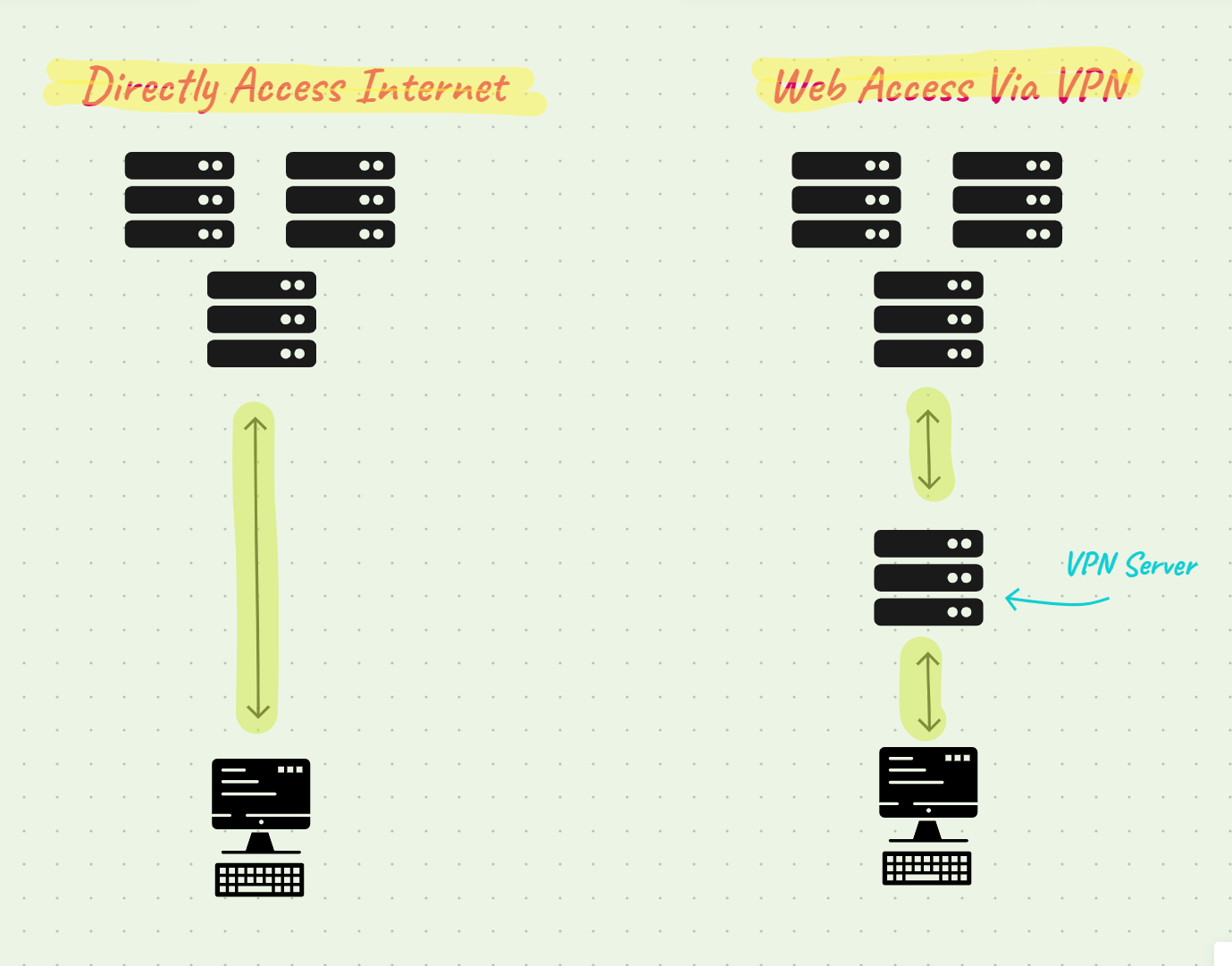
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) allows you to route your internet access through a specialized server that protects your sensitive data.
Accessing the internet (sending requests to servers) reveals your IP address directly, and public Wi-Fi networks can expose sensitive information such as passwords.
VPNs protect your data by routing requests through a proxy server that masks your location and information.
🚨You can either set up your own VPN server or use a third-party services.
Internal VPNs are used by some businesses to gain access to company services such as administrative tools.
How VPNs work
Internet & IP Location
Exposing your IP address online can lead to privacy risks and potential cyber threats.
Attackers may use your IP to track your online activities, launch targeted attacks, or attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in your network.
Additionally, disclosing your IP can make you susceptible to phishing attempts and unauthorized access to your devices.
VPN Types
At the core, there are two separate VPN classifications in terms of their usage, Personal VPNs and Company VPNs, which address distinct segments within an entity. Let's delve into the distinctions between the two:
Personnel VPNs
Personnel VPNs: Personnel VPNs, also known as consumer VPNs or personal VPNs, are services that individuals can use to enhance their online privacy and security. Regular users who want to protect their data from being intercepted by hackers typically used these or snooping ISPs, access geo-blocked content, or maintain their privacy while using public Wi-Fi networks. Key features of personnel VPNs include:
Data Encryption: Personnel VPNs encrypt the user's internet connection, making it difficult for third parties to intercept or decipher the data being transmitted.
Online Privacy: These VPNs hide the user's IP address, making it more difficult for websites and online services to track their online activities.
Geo-spoofing: Users can access websites and online content that might be restricted or geographically limited in their location by connecting to servers in different regions.
Public Wi-Fi Security: Personnel VPNs are commonly used on public Wi-Fi networks to add an extra layer of security and prevent potential eavesdropping.
Company VPN
Company VPNs: Company VPNs, also known as corporate VPNs or enterprise VPNs, are tools used by organizations to establish secure connections for their employees and sometimes partners or remote offices. Company VPNs are primarily designed to provide secure remote access to the organization's internal network and resources. Key features of company VPNs include:
Remote Access: Company VPNs allow employees to access internal resources like files, databases, and applications from remote locations as if they were directly connected to the organization's network.
Data Security: These VPNs provide a secure transmission channel for sensitive business data between remote employees and the company's internal network, thereby preventing potential breaches.
Authentication and Authorization: Multi-factor authentication is used by company VPNs to prevent unauthorized access. Multi-factor authentication ensures that only authorized individuals can access the network.
Data Control: Company VPNs allow organizations to maintain control over how their data is accessed, stored, and transmitted, which is crucial for compliance with data protection regulations.
Network Isolation: By using company VPNs, remote workers are connected to the organization's network, which helps maintain a level of isolation from potential security threats on the public internet.
To sum up, although personnel VPNs and company VPNs both establish secure connections over the internet, their objectives are distinct. Individuals utilize personnel VPNs to ensure privacy and access restricted content, whereas organizations employ company VPNs to ensure secure remote access to internal resources, preserving data security and control.
🚨From a technical standpoint, VPNs can be classified into distinct types based on protocols, network layers, and topology; such as site-to-site, point-to-point, point-to-site, etc.
Some VPNs has the ability to route internet traffic through servers located in different countries, potentially altering the perceived geographic location of the user.
📝Side Note
If you're wondering why it's so simple to find the location of an IP address, it's because the Regional Internet Registry is in charge of allocating and managing IP addresses all over the world, and they're dedicated to providing information transparency about each IP address. The Saudi Arabia (KSA) is serviced by a sub-organization known as RIPE NCC. Saudi Network Information Center (SaudiNIC) is the KSA domain registration authority. Since 1995, SaudiNIC has been managed and operated by King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST). The Communications, Space, and Technology Commission (CST) took over operation of SaudiNIC at the end of 2006.
Hi, I’m Wajid Khan. I am trying to explain computer stuff in a simple and engaging manner, so that even non-techies can easily understand, and delivered to your inbox weekly.